Personal Network Analysis - ppt download
4.5 (629) · $ 14.50 · In stock
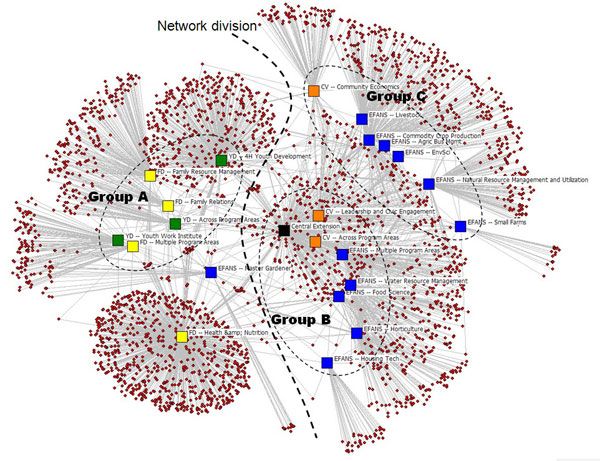
A bit of History … INSNA & Computers & Interdisciplinarity, NScience American Sociology (1976) Graph Theory (e.g. Harary 1963) Manchester School ( ) Moreno Sociometry (1934)
Christopher McCarty. University of Florida. Jose Luis Molina. Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona.
For instance … Gossip network … (Epstein, 1957)
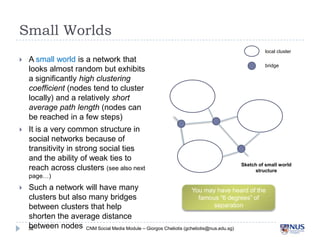
East York … (Wellman, 1999)
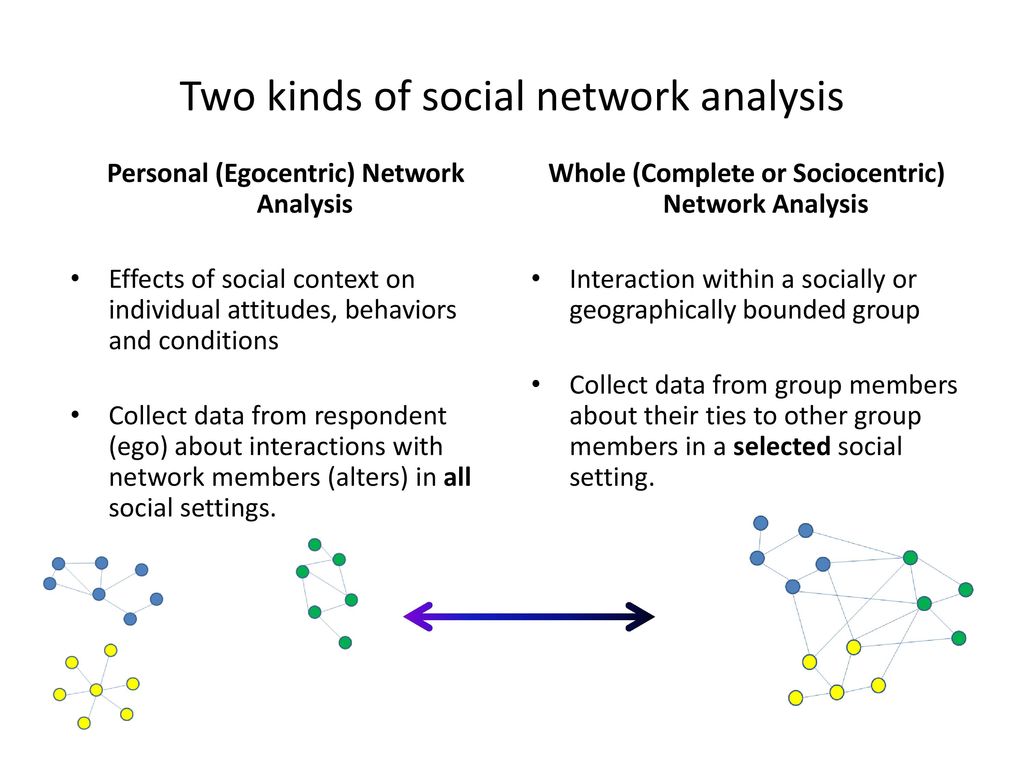
Personal (Egocentric) Network Analysis. Effects of social context on individual attitudes, behaviors and conditions. Collect data from respondent (ego) about interactions with network members (alters) in all social settings. Whole (Complete or Sociocentric) Network Analysis. Interaction within a socially or geographically bounded group. Collect data from group members about their ties to other group members in a selected social setting. Chris, I deleted some nodes in the whole network of the right because SOME NODES are not captured by the sociocentric networks (for instance, family …).
Example: Predict depression among seniors using the cohesiveness of their personal network. Social or geographic space. Social influence crosses social domains. Network variables are treated as attributes of respondents. These are used to predict outcomes (or as outcomes)
Focus on social position within the space. Social or geographic space. Example: Predict depression among seniors using social position in a Retirement Home.
Use overlapping networks as a proxy for whole network structure, and identify mutually shared peripheral alters. Social or geographic space. Example: Predict depression among seniors based on social position within a Retirement Home and contacts with alters outside the home.
Egocentric means focused on Ego . You can do an egocentric analysis within a whole network. See much of Ron Burt’s work on structural holes. See the Ego Networks option in Ucinet. Personal networks are egocentric networks within the whole network of the World (but not within a typical whole network).
If the phenomenon of interest occurs within a socially or geographically bounded space. If the members of the population are not independent and tend to interact. When to use personal networks. If the phenomena of interest affects people irrespective of a particular bounded space. If the members of the population are independent of one another. When to use both. When the members of the population are not independent and tend to interact, but influences from outside the space may also be important.
1. Introduction to. Personal Networks (ii). What are we measuring
Like snowflakes, no two personal networks are exactly alike. Social contexts may share attributes, but the combinations of attributes are each different. We assume that the differences across respondents influences attitudes, behaviors and conditions.
Ascribed characteristics. Sex. Age. Race. Place of birth. Family ties. Genetic attributes. Chosen characteristics. Income. Occupation. Hobbies. Religion. Location of home. Amount of travel.
Social outcomes. Personality. Acculturation. Well-being. Social capital. Social support. Health outcomes. Smoking. Depression. Fertility. Obesity.
1. Introduction to Personal Networks (iii). Types of personal network data.
Composition: Variables that summarize the attributes of alters in a network. Average age of alters. Proportion of alters who are women. Proportion of alters that provide emotional support. Structure: Metrics that summarize structure. Number of components. Betweenness centralization. Subgroups. Composition and Structure: Variables that capture both. E-I Index.
* Proportion of personal network that are women … *Average age of network alters … *Proportion of strong ties … * Average number of years knowing alters …
36 Percent Host Country. 44 Percent Host Country. Percent from host country captures composition. Does not capture structure.
Joydip_K. Shikha_K. Candice_A. Brian_N. Barbara_A. Matthew_A. Kavita_G. Ketki_G
Average degree centrality (density) Average closeness centrality. Average betweenness centrality. Core/periphery. Number of components. Number of isolates.
Components captures separately maintained groups (network structure) It does not capture type of groups (network composition)
SD Average Betweenness SD Betweenness centrality captures bridging between groups. It does not capture the types of groups that are bridged.
Goals, design, sampling, bias & name generators issues.
Personal network data are time-consuming and difficult to collect with high respondent burden. Sometime network concepts can be represented with proxy questions. Example: Do most of your friends smoke By doing a network study you assume that the detailed data will explain some unique portion of variance not accounted for by proxies. It is difficult for proxy questions to capture structural properties of networks.
Choose wisely, define properly – this largely will determine your modes of data collection and the sampling frame you will use to select respondents. Certain populations tend to cluster spatially, or have lists available, while others do not.
Face-to-face, telephone, mail, and Web (listed here in order of decreasing cost) The majority of costs are not incurred in actually interviewing the respondent, but in finding available and willing respondents. Depending on the population there may be no convenient or practical sample frame for making telephone, mail, or contact.
Name generators are questions used to elicit alter names. Elicitation will always be biased because: Names are not stored randomly in memory. Many variables can impact the way names are recalled. Respondents have varying levels of energy and interest.
The setting. Home. Work. The use of external aids. Phone. Address book. Facebook. Others sitting nearby. Serial effects to naming. Alters with similar names. Alters in groups. Chronology. Frequency of contact. Duration.
Large sample of alters. Name 45 alters. Force chronology. List alters you saw most recently. Diary. Force structure. Name as many unrelated pairs and isolates. Force closeness. Name people you talk to about important matters. Attempt randomness. Name people with specific first names.
Memory. Fatigue. Motivation. The number of alters listed is not a good proxy for network size. There are other ways to get network size. RSW. Network Scale-up Method. Structural metrics with different numbers of alters requires normalization. Sometimes is preferable to have respondents do the same amount of work.
Try to avoid having respondents make uninformed guesses about people they know. Still, some researchers argue it is really the respondents’ perception of their alters that influences their own attitudes and behaviors. Figuring out how well a person knows their alters and the nature of their relationships is the most challenging interpretive activity.
Research suggests that tie strength is best assessed using questions about closeness. People tend to be less close to people they do not like, even though they may know a lot about them. Asking how respondents know someone is also helpful – How did you meet (school, work, etc.)
Personal Network Visualizations Hand-Drawn vs. Structural
Network visualization lets you quickly identify relationships between several compositional and structural variables simultaneously. Visualization should be guided by research question. The way different software algorithms places nodes with respect to one another is meaningful. Nodes and ties can often be sized, shaped, and colored in various ways to convey info.
Approach of Juergen Lerner focusing on inter-group ties to create personal network types
Organization Network Analysis Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Styles
Social Network Analysis - ppt download

Personal Network Analysis - ppt download
Social Network Analysis

PPT - BLUETOOTH AS A PERSONAL AREA NETWORK PowerPoint Presentation
Social Network Diagram

Stakeholder Analysis Infographics Presentation Template
Social Network Analysis

Personal Network Analysis - ppt download

Personal Network Analysis - ppt download